Unit 2 Kinetics
2.6 Exercises
OpenStax
Section 2.6 Exercises
- Account for the increase in reaction rate brought about by a catalyst.
- Consider this scenario and answer the following questions: Chlorine atoms resulting from decomposition of chlorofluoromethanes, such as CCl2F2, catalyze the decomposition of ozone in the atmosphere. One simplified mechanism for the decomposition is:
[latex]\text{O}_3\;{\xrightarrow{\text{sunlight}}}\;\text{O}_2\;+\;\text{O} \\[0.5em] \text{O}_3\;+\;\text{Cl}\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{O}_2\;+\;\text{ClO} \\[0.5em] \text{ClO}\;+\;\text{O}\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{Cl}\;+\;\text{O}_2[/latex](a) Explain why chlorine atoms are catalysts in the gas-phase transformation:
[latex]2\text{O}_3\;{\longrightarrow}\;3\text{O}_2[/latex]
(b) Nitric oxide is also involved in the decomposition of ozone by the mechanism:
[latex]\text{O}_3\;{\xrightarrow{\text{sunlight}}}\;\text{O}_2\;+\;\text{O} \\[0.5em] \text{O}_3\;+\;\text{NO}\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{NO}_2\;+\;\text{O}_2 \\[0.5em] \text{NO}_2\;+\;\text{O}\;{\longrightarrow}\;\text{NO}\;+\;\text{O}_2[/latex]
Is NO a catalyst for the decomposition? Explain your answer. - For each of the following pairs of reaction diagrams, identify which of the pairs is catalyzed:
(a)
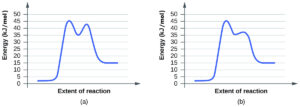
(b)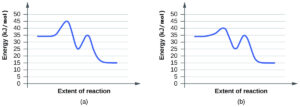
- For each of the following reaction diagrams, estimate the activation energy (Ea) of the reaction:
(a)
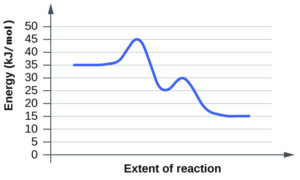
(b)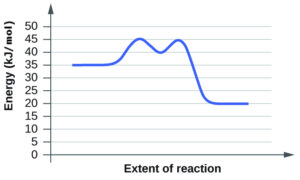
- Based on the diagrams in Exercise 4, which of the reactions has the fastest rate? Which has the slowest rate?
Solutions
- The general mode of action for a catalyst is to provide a mechanism by which the reactants can unite more readily by taking a path with a lower reaction energy. The rates of both the forward and the reverse reactions are increased, leading to a faster achievement of equilibrium.
- (a) Chlorine atoms are a catalyst because they react in the second step but are regenerated in the third step. Thus, they are not used up, which is a characteristic of catalysts.
(b) NO is a catalyst for the same reason as in part (a). - The lowering of the transition state energy indicates the effect of a catalyst.
(a) neither is catalyzed because the highest activation energy is the same in A and B
(b) B - The energy needed to go from the initial state to the transition state is
(a) 10 kJ
(b) 10 kJ - Both have the same activation energy, so they also have the same rate.

