Unit 4 Acid-Base and Solubility Equilibria
4.1 Definitions of Acids and Bases
OpenStax
Section Learning Objectives
- Identify acids, bases, and conjugate acid-base pairs according to the Brønsted-Lowry definition.
- Write equations for acid and base ionization reactions.
- Use the ion-product constant for water to calculate hydronium and hydroxide ion concentrations.
- Describe the acid-base behaviour of amphiprotic substances.
✓ SECTION 4.1 CHECKLIST
| Learning Activity | Graded? | Estimated Time |
|---|---|---|
| Make notes about this section’s reading portion. | No | 45 min |
| Optional Resource: Watch the video explanation of acid-base theory. | No | 4 min |
| Optional Activity: Explore the simulation on pH and the autoionization constant of water as a function of temperature. | No | 5 min |
| Work on the self-check question. | No | 10 min |
| Work on practice exercises. | No | 30 min |
📖 READING PORTION
Historical Development of Acid-Base Theory
The acid-base reaction class has been studied for quite some time. In 1680, Robert Boyle reported traits of acid solutions that included their ability to dissolve many substances, to change the colours of certain natural dyes, and to lose these traits after coming in contact with alkali (base) solutions. In the eighteenth century, it was recognized that acids have a sour taste, react with limestone to liberate a gaseous substance (now known to be CO2), and interact with alkalis to form neutral substances. In 1815, Humphry Davy contributed greatly to the development of the modern acid-base concept by demonstrating that hydrogen is the essential constituent of acids. Around that same time, Joseph Louis Gay-Lussac concluded that acids are substances that can neutralize bases and that these two classes of substances can be defined only in terms of each other. The significance of hydrogen was reemphasized in 1884 when Svante Arrhenius defined an acid as a compound that dissolves in water to yield hydrogen cations (now recognized to be hydronium ions) and a base as a compound that dissolves in water to yield hydroxide anions.
Johannes Brønsted and Thomas Lowry proposed a more general description in 1923 in which acids and bases were defined in terms of the transfer of hydrogen ions, H+. (Note that these hydrogen ions are often referred to simply as protons, since that subatomic particle is the only component of cations derived from the most abundant hydrogen isotope, 1H.) A compound that donates a proton to another compound is called a Brønsted-Lowry acid, and a compound that accepts a proton is called a Brønsted-Lowry base. An acid-base reaction is, thus, the transfer of a proton from a donor (acid) to an acceptor (base).
Acid-Base Reactions
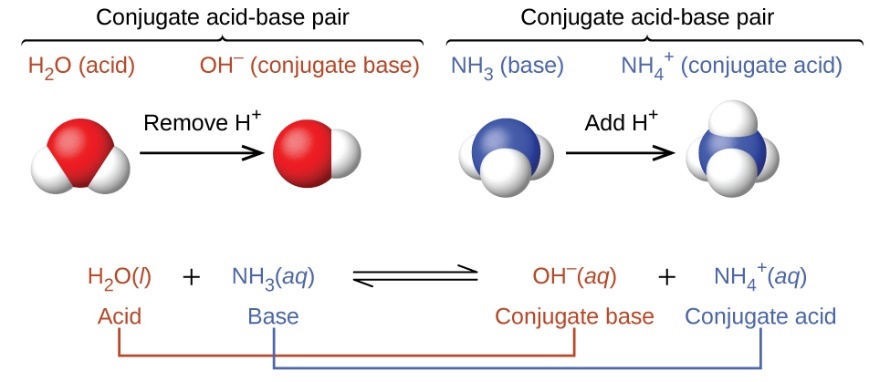
The concept of conjugate pairs is useful in describing Brønsted-Lowry acid-base reactions (and other reversible reactions, as well). When an acid donates H+, the species that remains is called the conjugate base of the acid because it reacts as a proton acceptor in the reverse reaction. Likewise, when a base accepts H+, it is converted to its conjugate acid. The reaction between water and ammonia illustrates this idea. In the forward direction, water acts as an acid by donating a proton to ammonia and subsequently becoming a hydroxide ion, OH−, the conjugate base of water. The ammonia acts as a base in accepting this proton, becoming an ammonium ion, NH4+, the conjugate acid of ammonia. In the reverse direction, a hydroxide ion acts as a base in accepting a proton from ammonium ion, which acts as an acid.
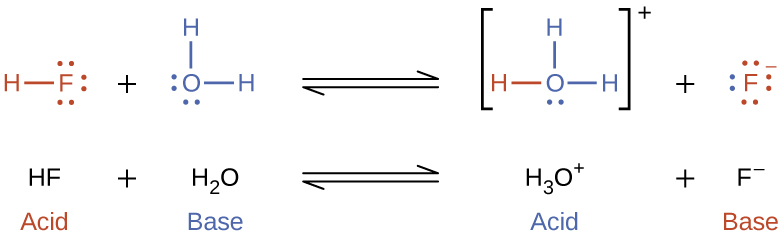
The reaction between a Brønsted-Lowry acid and water is called acid ionization. For example, when hydrogen fluoride dissolves in water and ionizes, protons are transferred from hydrogen fluoride molecules to water molecules, yielding hydronium ions and fluoride ions.
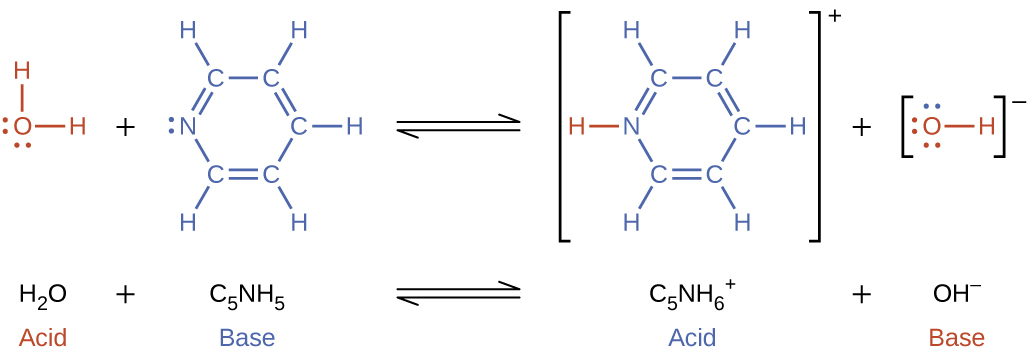
Base ionization of a species occurs when it accepts protons from water molecules. In the example below, pyridine molecules, C5NH5, undergo base ionization when dissolved in water, yielding hydroxide and pyridinium ions.
The preceding ionization reactions suggest that water may function as both a base (as in its reaction with hydrogen fluoride) and an acid (as in its reaction with ammonia). Species capable of either donating or accepting protons are called amphiprotic, or more generally, amphoteric, a term that may be used for acids and bases per definitions other than the Brønsted-Lowry one, such as the Lewis definition of acids and bases from CHEM 1500/1503. The equations below show the two possible acid-base reactions for two amphiprotic species, bicarbonate ion and water.
HCO3–(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ CO32–(aq) + H3O+(aq)
HCO3–(aq) + H2O(l) ⇌ H2CO3(aq) + OH–(aq)
The first equation represents the reaction of bicarbonate as an acid with water as a base, whereas the second represents the reaction of bicarbonate as a base with water as an acid. When bicarbonate is added to water, both these equilibria are established simultaneously and the composition of the resulting solution may be determined through appropriate equilibrium calculations, as described later in Section 4.2.
In the liquid state, molecules of an amphiprotic substance can react with one another as illustrated for water in the equations below.
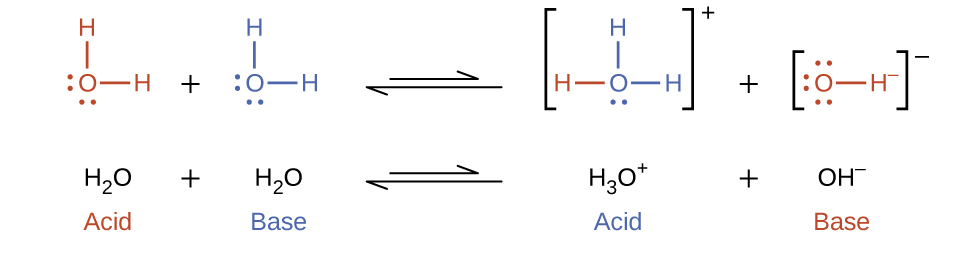
The process in which like molecules react to yield ions is called autoionization. Liquid water undergoes autoionization to a very slight extent; at 25°C, approximately two out of every billion water molecules are ionized. The extent of the water autoionization process is reflected in the value of its equilibrium constant, the ion-product constant for water, Kw.
H2O(l) + H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + OH−(aq) Kw = [H3O+][OH−]
The slight ionization of pure water is reflected in the small value of the equilibrium constant; at 25°C, Kw has a value of 1.0 × 10−14. For CHEM 1523, the acid-base questions we cover will be at 25°C unless otherwise specified. The Kw equation is thus equal to the constant 1.0 × 10−14.
Equation 1
Kw = 1.0 × 10−14 = [H3O+][OH−]
The process is endothermic, and so the extent of ionization and the resulting concentrations of hydronium ion and hydroxide ion increase with temperature. For example, at 100°C, the value for Kw is about 5.6 × 10−13, roughly 50 times larger than the value at 25°C.
Example 1
Ion Concentrations in Pure Water
What are the hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide ion concentration in pure water at 25°C?
SOLUTION
The autoionization of water yields the same number of hydronium and hydroxide ions. Therefore, in pure water, [H3O+] = [OH−] = x. At 25°C,
[latex]K_{\text{w}} = [\text{H}_3\text{O}^+][\text{OH}^−] = (x)(x) = x^2 =1.0×10^{−14}[/latex]
[latex]x = [\text{H}_3\text{O}^+] = [\text{OH}^−] = \sqrt{1.0×10^{−14}} =1.0×10^{−7}\text{ M}[/latex]
The hydronium ion concentration and the hydroxide ion concentration are the same, 1.0 × 10−7 M.
Example 2
The Inverse Relation between [latex][\text{H}_3\text{O}^+] \text{and} [\text{OH}^−][/latex]
A solution of an acid in water has a hydronium ion concentration of 2.0 × 10−6 M. What is the concentration of hydroxide ion at 25°C?
SOLUTION
Use the value of the ion-product constant for water at 25°C
2 H2O(l) ⇌ H3O+(aq) + OH−(aq) Kw = [H3O+][OH−] = 1.0 × 10−14
to calculate the missing equilibrium concentration. Rearrangement of the Kw expression shows that [OH−] is inversely proportional to [H3O+].
[latex][\text{OH}^−] = \frac{K_{\text{w}}}{[\text{H}_3\text{O}^+]} = \frac{1.0×10^{−14}}{2.0×10^{−6}} = \boxed{5.0×10^{−9} \text{ M}}[/latex]
Compared with pure water, a solution of acid exhibits a higher concentration of hydronium ions (due to ionization of the acid) and a proportionally lower concentration of hydroxide ions. This may be explained via Le Châtelier’s principle as a left shift in the water autoionization equilibrium resulting from the stress of increased hydronium ion concentration.
Substituting the ion concentrations into the Kw expression confirms this calculation, resulting in the expected value
[latex]K_{\text{w}} = [\text{H}_3\text{O}^+][\text{OH}^−] = (2.0×10^{−6})(5.0×10^{−9}) = 1.0×10^{−14}[/latex]
Example 3
Representing the Acid-Base Behaviour of an Amphoteric Substance
Write separate equations representing the reaction of HSO3−(aq)
(a) as an acid with OH−(aq)
(b) as a base with HI(aq)
SOLUTION
(a) HSO3−(aq) + OH−(aq) ⇌ SO32−(aq) + H2O(l)
(b) HSO3−(aq) + HI(aq) ⇌ H2SO3(aq) + I−(aq)
Optional Resource
Watch this video explanation of acid-base theory.
Video 1 What Is The Bronsted Lowry Theory (3 min 56 s).
Optional Activity
The extent of the autoionization of water varies with temperature. Use this simulation to determine the pH of neutral solution and Kw from 1 to 99 °C.
Which of the following statements is true about ammonia (NH3)?
A) NH4+ is its conjugate acid; NH2– is its conjugate base.
B) NH4+ is its conjugate acid; it has no conjugate base.
C) It has no conjugate acid; NH2– is its conjugate base.
D) It has neither a conjugate acid or conjugate base.
Click to see answer
A) NH4+ is its conjugate acid; NH2– is its conjugate base.

